High disk latency in SAN (Storage Area Network) or DAS (Direct-Attached Storage) environments can stem from various issues. Here’s a breakdown to help troubleshoot:
1. Common Causes of High Disk Latency
SAN:
- Network Bottlenecks:
- High I/O traffic saturating the SAN fabric (e.g., Fibre Channel or iSCSI network).
- Misconfigured switches, cables, or ports causing retransmissions.
- Storage Controller Overload:
- Storage controllers may be overwhelmed by too many concurrent requests.
- Improper LUN Configuration:
- Misaligned or poorly optimized LUNs (Logical Unit Numbers) causing performance hits.
- Disk Tiering Issues:
- Data may be stuck on slower tiers (e.g., spinning disks instead of SSDs).
- Latency at Host Level:
- Queue depth settings (HBA or multipathing configuration) may limit throughput.
DAS:
- Disk Spindle Speed:
- If relying on HDDs, lower spindle speeds (e.g., 5400 or 7200 RPM) may struggle with high loads.
- RAID Rebuilds or Failures:
- Ongoing RAID rebuilds can degrade performance significantly.
- Single Point of Failure:
- DAS setups often rely on fewer redundancy mechanisms than SAN.
2. How to Identify the Root Cause
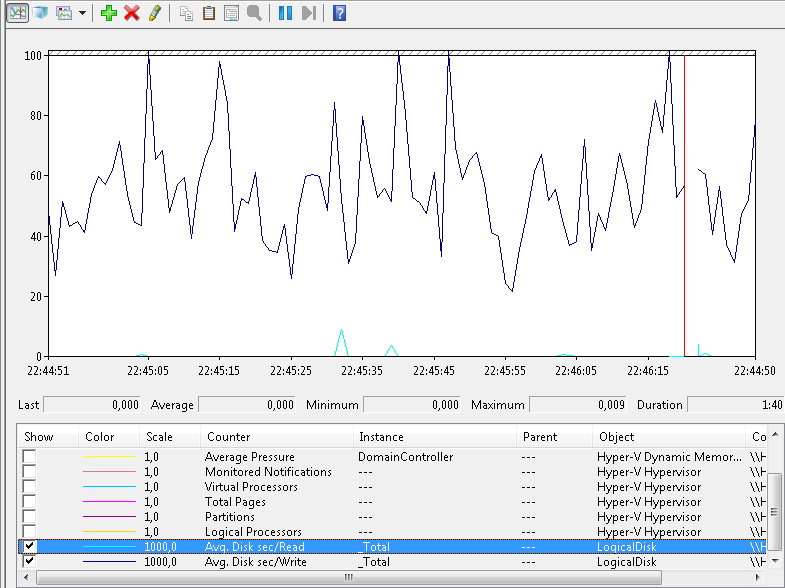
- Check Latency Metrics:
- For SAN: Use tools like VMware vSphere, SANtricity, or vendor-specific utilities (e.g., Dell EMC Unisphere, NetApp ONTAP).
- For DAS: Use OS-level utilities like
iostat,top, orperfmon.
- Analyze I/O Patterns:
- Determine if the issue is due to random I/O or sequential workloads.
- Inspect Queue Depth:
- Use tools like
esxtop(for VMware) to review storage queue metrics.
- Use tools like
- Verify Network Health (For SAN):
- Look for dropped packets or CRC errors in Fibre Channel or iSCSI paths.
3. Solutions
For SAN:
- Optimize Pathing:
- Enable multipathing (e.g., Round Robin, Fixed, or Adaptive settings based on your SAN vendor).
- Increase Queue Depth:
- Adjust queue depth settings on the HBA and storage side.
- Network Optimization:
- Ensure jumbo frames are enabled for iSCSI.
- Check switch configurations for congestion or errors.
- Tiering & Cache:
- Use SSD caching or auto-tiering to move “hot” data to faster media.
For DAS:
- RAID Configuration:
- Use RAID levels optimized for performance (e.g., RAID 10 over RAID 5 for heavy write workloads).
- Disk Replacement:
- Upgrade to SSDs or NVMe drives if still using spinning disks.
- Driver Updates:
- Ensure firmware and drivers for the disk controllers are up to date.
4. When to Escalate
- If internal troubleshooting doesn’t resolve the issue, engage:
- Storage Vendor Support: For SAN or DAS firmware, hardware, or advanced diagnostics.
- Networking Team: For SAN fabric issues.
- Application Team: To validate if the workload is improperly optimized.
To find out about our services,
- Contact us.